29-01-2024 - Physics - The mechanical energy equation [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
29-01-2024 - Physics - The mechanical energy equation [EN]-[IT]
The mechanical energy equation
Basic concepts
For the topic in question it is good to know that the first law of thermodynamics for open systems establishes that the energy associated with a control mass (M.C.) can vary over time due to two different types of energy flows:
-Thermal power
-Mechanical power
Instead, the second law of thermodynamics for open systems states that the entropy associated with a control mass can vary due to entropic flow and entropy production.
Summing up:
The first law of thermodynamics on open systems speaks of the energy associated with the control mass, while the second law speaks of the entropy associated with the control mass.
The mechanical energy equation
Let's always imagine we have the following system
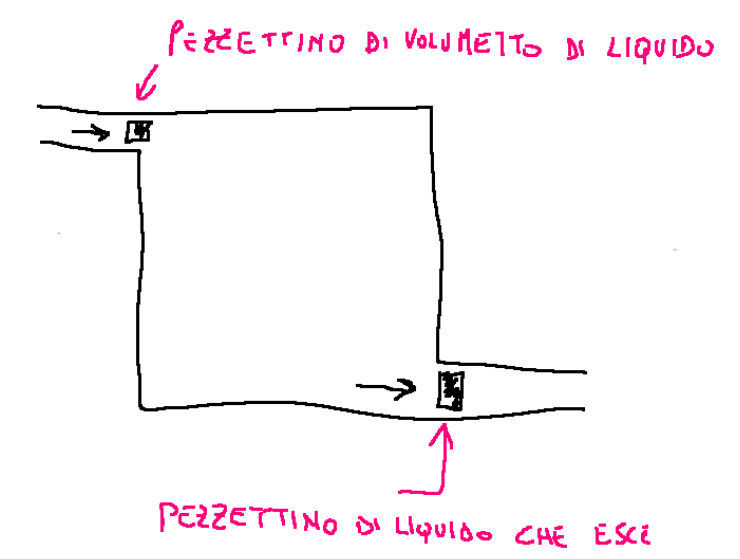
The first law of thermodynamics for open systems
The first law of thermodynamics for open systems in steady state conditions is as follows
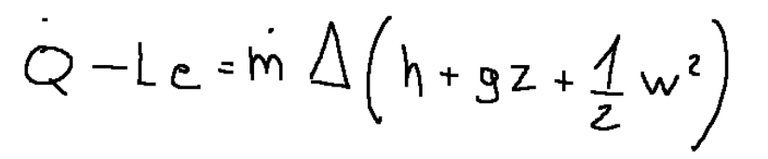
Mechanical energy equation
The mechanical energy equation can be derived from the formula expressed above and is as follows.
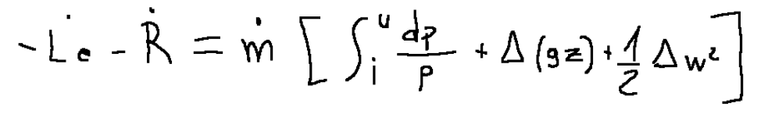
Where:
Le = propeller mechanical power. That is, the work exchanged between system and environment through the use of a rotating shaft.
R is a term related to internal energy production
Now let's assume that:
ρ = const, i.e. the flowing medium is also a perfect liquid.
L e is equal to zero (L e = 0), this would mean that there is no organ that transfers work in the system.
R= 0, i.e. there is no friction between the fluids and the walls of the system.
At this point we obtain the following formula:
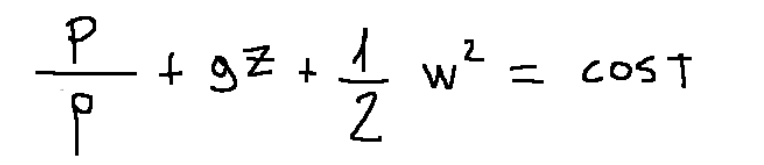
This formula relating to the motion of the inviscid fluid in stationary cases, with a single inlet and a single outlet, in the absence of propeller work and friction, coincides with the Bernoulli equation.
Conclusions
By adding particular conditions to the mechanical energy equation, we can derive a formula that coincides with the Bernoulli equation relating to the motion of a fluid.
Request
Do you remember studying these concepts at school? These are concepts that are not always taught in schools.

29-01-2024 - Fisica - L’equazione dell’energia meccanica [EN]-[IT]
L’equazione dell’energia meccanica
Concetti base
Per l'argomento in questione è bene sapere che la prima legge della termodinamica per i sistemi aperti stabilisce che l'energia associata ad una massa di controllo (M.C.) può variare nel tempo a causa di due differenti tipi di flussi energetici:
-Potenza termica
-Potenza meccanica
Invece la seconda legge della termodinamica per i sistemi aperti stabilisce che l'entropia associata ad una massa di controllo può variare a causa del flusso entropico e della produzione di entropia.
Riassumendo:
La prima legge della termodinamica sui sistemi aperti parla dell'energia associata alla massa di controllo, mentre la seconda legge parla dell'entropia associata alla massa di controllo.
L’equazione dell’energia meccanica
Immaginiamo sempre di avere il seguente sistema

La prima legge della termodinamica per i sistemi aperti
La prima legge della termodinamica per i sistemi aperti in condizioni stazionarie è la seguente
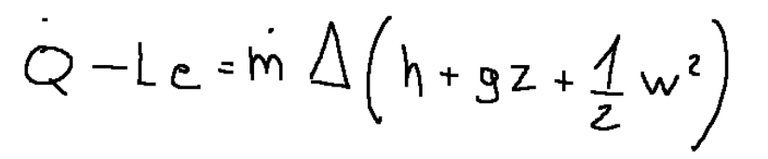
Equazione dell’energia meccanica
L’equazione dell’energia meccanica può essere derivata dalla formula espressa sopra ed è la seguente.
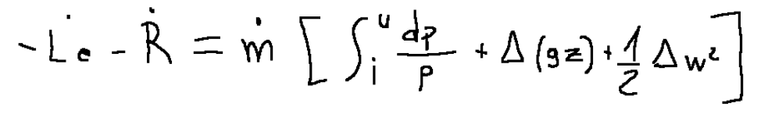
Dove:
Le = potenza meccanica d’elica. Cioè il lavoro scambiato tra sistema e ambiente attraverso l’utilizzo di un albero rotante.
R è un termine legato alla produzione di energia interna
Ora ipotizziamo che:
ρ = cost, cioè il mezzo che fluisce è anche un liquido perfetto.
L e sia uguale a zero (L e = 0), questo significherebbe che non c’è alcun organo che trasferisce lavoro nel sistema.
R= 0, cioè che non ci sono attriti tra i fluidi e le pareti del sistema.
A questo punto otteniamo la seguente formula:
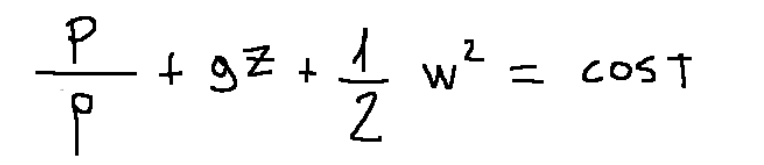
Questa formula relativa al moti del fluido non viscoso nei casi stazionari, con un solo ingresso ed una sola uscita, in assenza di lavoro d’elica e di attriti, coincide con l'equazione di Bernoulli.
Conclusioni
Aggiungendo delle condizioni particolari all'equazione dell'energia meccanica, possiamo ricavare una formula che coincide con l'equazione di Bernoulli relativa al moto di un fluido.
Domanda
Questi concetti ricordate di averli studiati a scuola? Sono concetti che non sempre vengono insegnati nelle scuole.
THE END
Congratulations @stefano.massari! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
Physics has been one of my favourite subjects and course and it is glad to see it happening that I am still seeing a lot from it
In this case we can also talk about the Benoulli equation, i.e. the one relating to the motion of a non-viscous fluid in stationary cases, with a single input and a single output, in the absence of propeller work and friction.
Thanks for sharing this interesting physics lesson that applies the laws of thermodynamics to open systems. The Bernoulli equation you talked about reminds me of the Bernoulli family composed of renowned mathematicians I wonder which one of them came up with the equation. Have a great day.
Daniel Bernoulli was a Swiss mathematician and physicist, one of the most important members of the Bernoulli family. The Bernoullis were very intelligent people. I mentioned Daniel Bernoulli before because he is the physical Bernoulli known in fluid dynamics. Thanks for your support
Thank you very much for this class
I was able to learn!
in trying to derive the mechanical energy equation we come across a formula that coincides with the Bernoulli equation which is the following
Physics always one of my favourite subjects then
Below is the mechanical energy equation. I admit that written like this it seems really complicated.
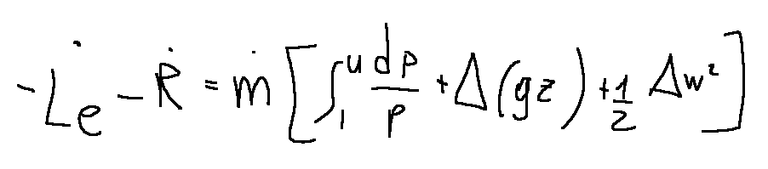
Questo è legato alla meccanica dei fluidi, non ne sono molto sicuro, questo argomento corrisponde più a chi studia ingegneria meccanica all'università, questo lo so da alcuni colleghi, ma non conosco l'argomento
esatto infatti possiamo anche parlare in questo caso di Bernoulli. L'equazione di Bernoulli, cioè quella relativa al moto di un fluido non viscoso nei casi stazionari, con un solo ingresso ed una sola uscita, in assenza di lavoro d'elica e di attriti.