02-01-2024 - Physics - Differential operators [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
02-01-2024 - Physics - Differential operators [EN]-[IT]
Differential Operators
Basic concepts
The operators that we will see later are used in thermodynamic studies. Below we reiterate some basic concepts of thermodynamics.
Anergotic surfaces are surfaces that do not allow workflows.
An adiabatic surface is a surface that does not allow heat exchange.
The diathermic surface is a surface that allows heat flows.
Differential operators
The differential operator is an operator defined as a function of the differentiation operator. In the sentence just written we clarify the terms operator and derivation.
Operator: its meaning is connected to the notion of function
Derivation: construct a derivative, that is, express the variation of one quantity with respect to another.
Among the differential operators we have the gradient, the divergence and the Laplacian:
The gradient
The gradient of a variable is an operator that transforms a scalar into a vector.
If we take the temperature T as an example, we can say that we will have the direction of the vector which will be the one for which the maximum variation of T is found, while the modulus will be represented precisely by this variation.
To represent a gradient we need another operator called NABLA.
Below is the representation of the NABLA operator.
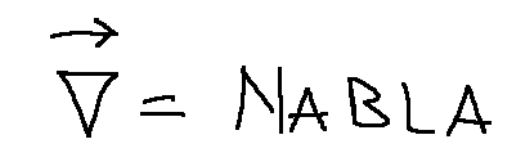
Note: The symbol NABLA is used in mathematics and in particular in vector calculus and mathematical analysis.
Below is a representation of the differential operator called gradient.
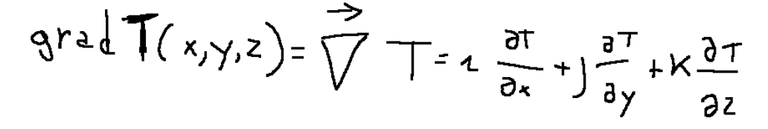
The divergence
The divergence of a vector, as opposed to the gradient, is an operator that transforms a vector into a scalar.
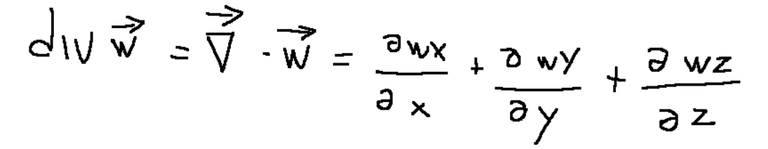
The Laplacian
The Laplacian (pronounced Laplacian in Italian) of a variable is the scalar product between the vector operator nebla and its gradient. The Laplacian can be described mathematically as it is represented below.
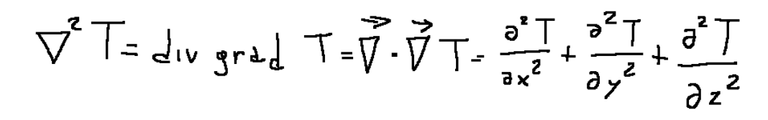
Or it can also be defined like this:
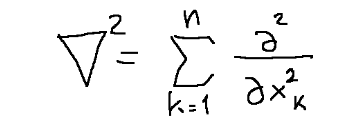
Note:
In this link you can find some information about the gradient:
https://www.univpm.it/Entra/Engine/RAServeFile.php/f/P002340/allegati_ins/nabla_stokes.pdf
In this link you can find some information about the nebla operator:
https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operatore_nabla
Conclusions
The best-known differential operators are the gradient, the divergence and the Laplacian.
Request
Have you ever used these differential operators? Do you find the use of these operators complicated?

01-02-2024 - Fisica - Operatori differenziali [EN]-[IT]
Operatori differenziali
Concetti base
Gli operatori che vedremo in seguito sono usati nell'ambito degli studi termodinamici. Qui di seguito ribadiamo alcuni concetti base della termodinamica.
Le superfici anergotiche sono superfici che non consentono flussi di lavoro.
Le superficie adiabatica è una superficie che non consente lo scambio di calore.
La superficie diatermica è una superficie che consente flussi di calore.
Operatori differenziali
L'operatore differenziale è un operatore definito come una funzione dell'operatore di derivazione. Nella frase appena scritta chiariamo il termine operatore e derivazione.
Operatore: il suo significato è collegato alla nozione di funzione
Derivazione: costruire una derivata, cioè esprimere la variazione di una grandezza rispetto ad un'altra.
Tra gli operatori differenziali abbiamo il gradiente, la divergenza e il laplaciano:
Il gradiente
Il gradiente di una variabile è un operatore che trasforma uno scalare in un vettore.
Se prendiamo come esempio la temperatura T, possiamo dire che avremo la direzione del vettore che sarà quella per cui si trova la massima variazione di T, mentre il modulo sarà rappresentato proprio da questa variazione.
Per rappresentare un gradiente abbiamo bisogno di un altro operatore detto NABLA.
Qui di seguito la rappresentazione dell’operatore NABLA.
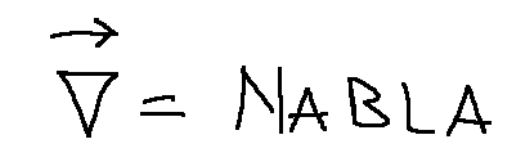
Nota: Il simbolo NABLA viene usato in matematica ed in particolare nel calcolo vettoriale e nell'analisi matematica.
Qui di seguito una rappresentazione dell’operatore differenziale chiamato gradiente.
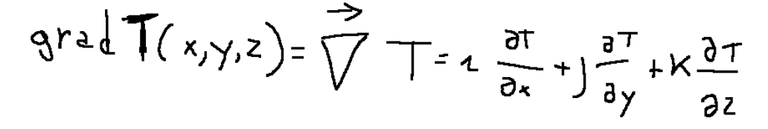
La divergenza
La divergenza di un vettore, al contrario del gradiente, è un operatore che trasforma un vettore in uno scalare.
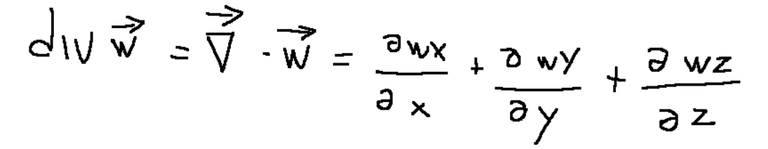
Il laplaciano
Il laplaciano (in italiano si pronuncia laplasiano) di una variabile è il prodotto scalare tra l'operatore vettoriale nebla ed il suo gradiente. Il laplaciano si può descrivere matematicamente come è rappresentato qui sotto.
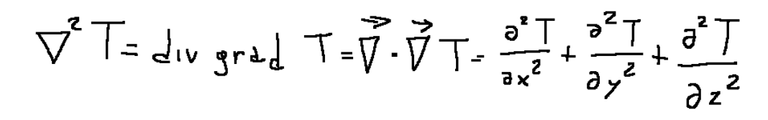
Oppure può essere definito anche così:
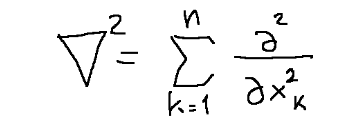
Note:
In questo link si possono trovare delle nozioni a riguardo del gradiente:
https://www.univpm.it/Entra/Engine/RAServeFile.php/f/P002340/allegati_ins/nabla_stokes.pdf
In questo link si possono trovare delle nozioni a riguardo dell'operatore nebla:
https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operatore_nabla
Conclusioni
Gli operatori differenziali più conosciuti sono il gradiente, la divergenza e il laplaciano.
Domanda
Avete mai usato questi operatori differenziali? Trovate complicato l'uso di questi operatori?
THE END
I think I read about operators once but that was in maths. I also know a little about scalars and vectors. The lesson was interesting, I caught a few things. Thanks for sharing and have a great day.
Differential operators are starting to be a difficult thing for me. However, in mathematics a differential operator is an operator defined as a function of the differentiation operator, while in physics they work on physical quantities
This is my first time hearing of Laplacian
Physics is indeed a wide course and has some bit of mathematics in it
Among the differential operators we find the gradient of a variable. This transforms a scalar into a vector. If we take temperature as an example, the gradient finds the direction of the vector where the maximum temperature variation is found, while the module represents precisely this variation. However for me differential operators in physics are quite difficult to understand
@tipu curate 2
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 8/48) Liquid rewards.
Grazie per il tipu Robby. Ho bisogno del tuo sostegno perché per fare questi post tecnici sto perdendo qualche follower, come da previsione. Il mio intento comunque rimane quello di provare a fare dei contenuti tecnici da immettere qui su HIVE
!discovery 25
grazie per la segnalazione
Ammetto che per quanto riguarda gli operatori differenziali, faccio un poco a fatica a digerirli. A parte il gradiente e la divergenza, gli altri fatico a comprenderli. Il gradiente si può applicare ad una variabile, mentre la divergenza ad un vettore.
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
One of the quality types of differential equations I really feared most
Yes!!!1 I too am afraid of differential operators. Let's say that the main ones can be the gradient and the divergence.
The gradient of a variable, such as temperature, is an operator that transforms a vector into a scalar. The divergence of a vector, in contrast, is an operator that transforms a vector into a scalar.
Non l'ho usato.
Ti auguro una felice giornata
Gli operatori differenziali più usati sono il gradiente, la divergenza ed il laplaciano, ma ammetto che anch'io durante il mio periodo scolastico li ho usati poco. Di questo articolo la cosa più interessante credo che siano il gradiente e la divergenza. Praticamente possiamo dire che uno è l'opposto dell'altro. Il gradiente di una varabile è un operatore che trasforma uno scalare in un vettore, mentre la divergenza di un vettore è un operatore che trasforma un vettore in uno scalare.
What an interesting topic to really digest and read of
The topic is not simple. I find differential operators in physics quite complicated. What is easiest for me to understand is the gradient. The gradient of a variable, such as temperature, is an operator that transforms a scalar into a vector, the direction of the vector is that for which the maximum variation of T is found, while the modulus represents precisely this variation. Thanks for stopping by